Unitized panels with enhanced thermal and acoustic performance (C.001)
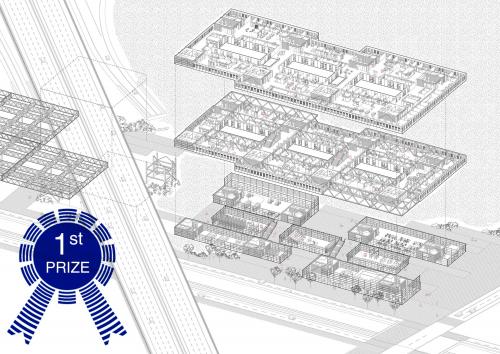
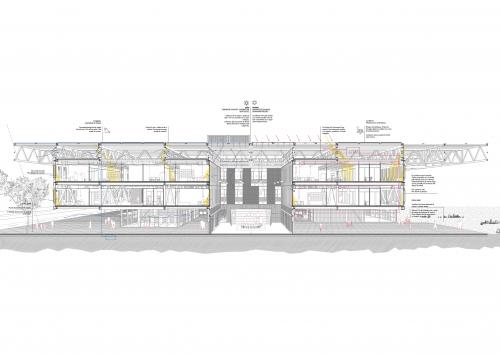
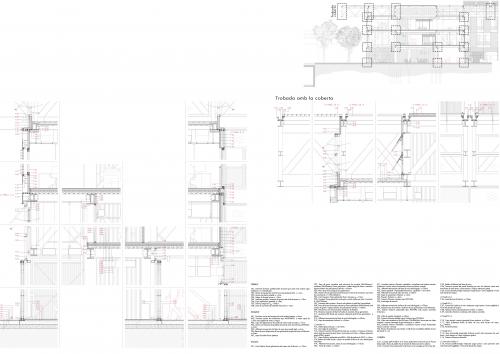
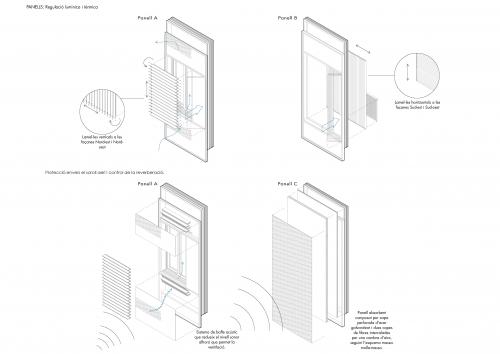
PROJECT'S CONTEXT This project tries to rethink the role of the Gran Via and the relationship between the different urban areas approaching El Prat to l'Hospitalet. A series of structural modules are proposed as a base to which trusses can be added.The module could be implemented in other places as a roof that’s able to collect water and produce energy. Responding to the changing needs of the infrastructure, the new building, which is going to host the new Technology Park, is a flexible space where the facilities and construction solutions are based on the Plug&Play system. Moreover, industrialization and dry assembly are applied to all aspects of the project, including the facade, in order to reduce site waste production and foster its component’s reuse. Furthermore, the facade contributes to optimising the energy use of the building. The user can also interact with the facade by manually moving its components to achieve both thermal and acoustic comfort. ITS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTIONS The project clearly distinguishes between the upper floors’ facade, which corresponds to office activity, and the ground floor's facade, becoming spaces of different character and offering an image of duality that will invert/shift from day to night. The ground floor's facade is composed by a galvanized steel substructure and a cellular polycarbonate. These components work as huge sliding doors which allow ground floor shops and workspaces to be opened and become thermally controlled recreational spaces, or to transform the restaurant into a terrace. The materiality of the facade blurs the interior/exterior relation resembling the structure of greenhouses. The upper facade is composed by individual panels assembled in a workshop. Its’ structure is made from extruded aluminium with thermal break and sealed with EPDM rubber. These panels, depending on their placement (panel A is for the external facade, and panels B and C are for the courtyard facade) have different material compositions and functions. Panel A is placed in exterior facades and its main function is to allow natural ventilation while reducing sound pollution to achieve good acoustic conditions for the office programme. This is achieved by integrating an acoustic baffle into the panel plus a drilled metal sheet. Air enters the baffle through the metal sheet, changes its sound frequency, and flows between absorbing panels losing energy and therefore, sound. During winter, this baffle may be closed, generating a double-glazed panel with an air chamber. In addition, direct ventilation can enter through an insulated opening and sun radiation can be regulated by external louvers. Panels B and C are combined in the courtyard's facades. On one hand, panel B allows ventilation and natural lighting control by a glazed finishing and an interior aluminium shutter. Its simplicity is possible due to its position in the building; the atrium acts as a sound and climate controlled intermediate space. On the other hand, panel C's function is to reduce the reverberation time in the atrium in order to use this space as a workshop. That is possible by a mass-spring-mass system made by a drilled metal sheet and two absorbing panels separated by an air chamber.